STRUCTURE OF COFFEE CHERRIES
Popular types of coffee in Vietnam
The tropical monsoon climate in Vietnam is very suitable for growing coffee trees, especially high-quality coffee varieties such as: Arabica, Robusta, Cherry.
Arabica Coffee

Arabica belongs to the Rubiaceae family, Coffea genus, in Vietnamese it is called Tea coffee due to its characteristics of small leaves and low stems like the tea tree in Vietnam. Arabica originated from southwestern Ethiopia, then followed the French to Vietnam. This is the first type of coffee grown in our country.
In the coffee family, Arabica has many different varieties and almost all of them are the best types of coffee. Some names include: Typica, Bourbon, Moka, Caturra, Mundo Novo, Catuai, Catimor, Moka
Arabica coffee is only suitable at the right height. Although it has low yields, it has a special aroma.
Robusta Coffee

Up to 39% of coffee production in the world is Robusta. This plant has a common origin with Arabica in Ethiopia but in the past it often grew in wild places. That's why Robusta trees are taller, have more branches and larger leaves than Arabica.
The taste of Robusta is not as highly appreciated as Arabica in terms of purity and natural aroma. So the price is only half that of the competition. However, the outstanding feature of this coffee variety is its very high caffeine content, accounting for about 2 - 4% of coffee beans while Arabica only has 1 - 3%.
Robusta has good disease resistance, high yield, and especially has a higher caffeine content than Arabica.
Cherry Coffee

Cherry, also known as Chari coffee, Jackfruit coffee originates from Ubangui Chari, near the world's largest desert, the Sahara. That's why this plant is quite tall, has large stems and leaves to store water, and can grow well in dry climates.
Chari's fruit is larger than other varieties but the yield is not high. In terms of taste, it is not as highly appreciated as Arabica or Robusta, so it is grown very little in our country today.
In addition to the coffee varieties mentioned above, there is also the mutant Culi line, which has both the flavors of Arabica and Robusta coffee.
Coffee flowers
The flower structure of the coffee tree is white and has 5 petals, not blooming individually but in large clusters. Coffee flowers have a very short pollination time, about 3 to 4 hours, but can bloom for up to 4 days.
Unlike many industrial plant varieties in Vietnam, the flowers of the coffee tree bloom many times a year. However, more or less depends on weather and climate conditions. Today there are many methods to naturally stimulate flower blooming to increase coffee production.
Coffee flowers only germinate in low temperature conditions or are provided with water after a dry period lasting about 2 to 3 months. Normally, seasons with hot weather alternating with rain after a few months will help coffee flowers bloom at the right time, giving higher yields.
Coffee flowers, in addition to bearing fruit to form coffee beans, also produce honey.
Knowing the blooming principle of coffee flowers, growers will have appropriate measures to provide water and nutrients to increase crop productivity. However, you should be careful to avoid bad weather, prolonged rain, especially frost, which will cause coffee flowers to rot, significantly reducing productivity.
Structure and composition of coffee beans
Structure of coffee beans
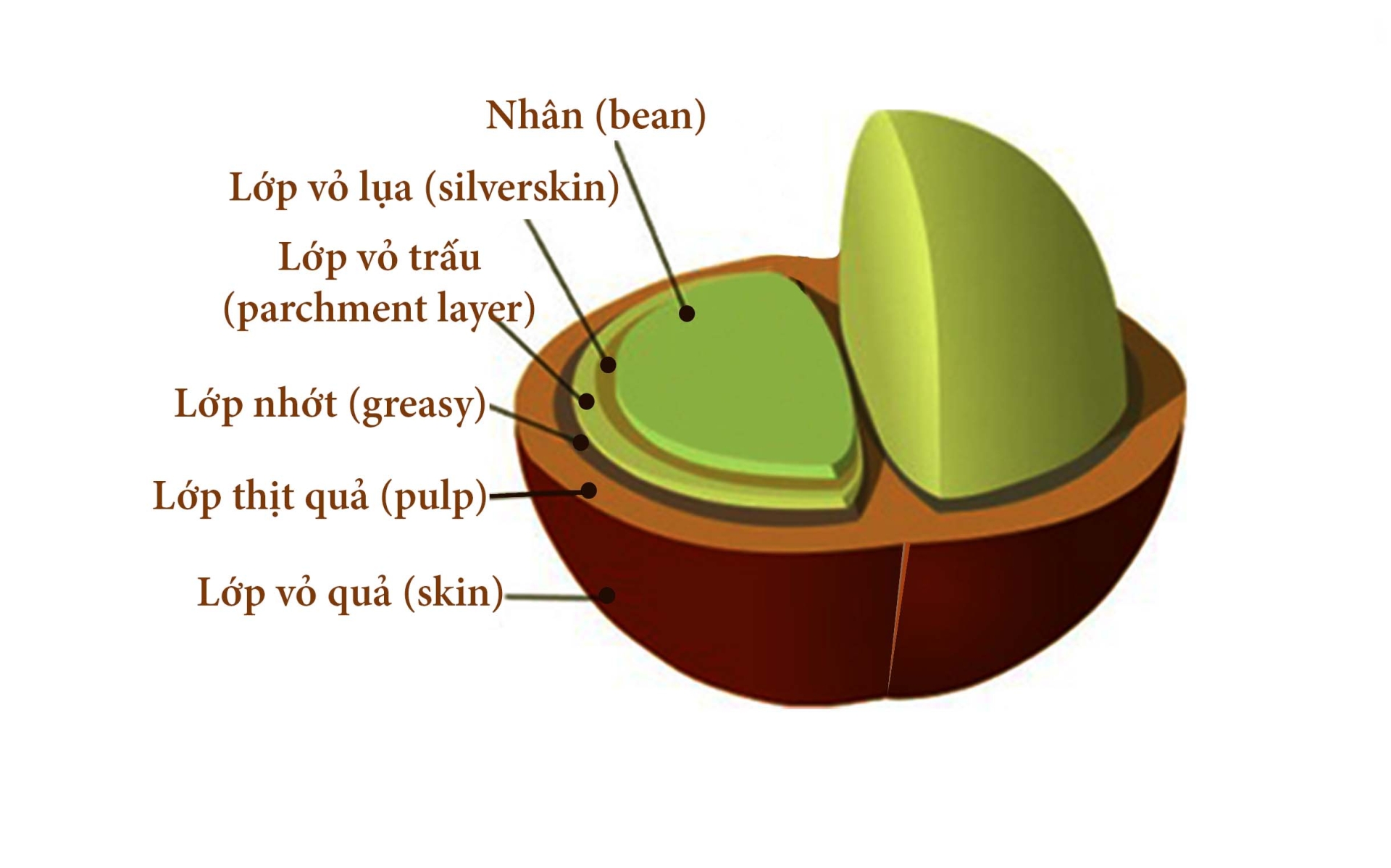
Structure of coffee beans
In a coffee fruit, there are 6 main parts: stem, fruit shell, flesh shell, husk, silk shell and kernel, also known as coffee beans.
The coffee stem
As the connection between the fruit and the tree branch, the coffee stem needs to be flexible. This helps prevent the coffee cherries from falling due to natural external impacts, but must be crispy for easy harvesting.
Peel
This is the outermost layer of the coffee fruit, with the function of covering and protecting the inside. When unripe, the coffee skin will be green and when ripe it will gradually turn red or yellow depending on the coffee variety. The shell of Arabica varieties will be softer and smaller than Robusta and Chari.
Meat shell
The flesh of the coffee pod has a mild sweet taste and can be eaten. In making Weasel coffee, the weasel will eat and absorb the meat shell and expel the core. The flesh of Arabica has the sweetest and softest taste, while Chari coffee has the thicker flesh.
Coffee beans are composed of many different layers.
The husk part
This is a rather hard shell after being dried to protect the coffee beans. After harvesting coffee, people will remove the outer skin. The flesh and slime are left behind, leaving only the husk and seeds inside. When processing, this layer of rice husk is also removed and can be used as fuel and composted very well.
Silk shell
The silk skin is a very thin and soft part that wraps around the coffee bean. Each type of coffee has a different skin color. Accordingly, the skin of Arabica coffee is white, Robusta coffee is light brown and the silk skin of Chari coffee is light yellow.
Coffee filling
This is the ingredient that creates value for the coffee tree. The coffee bean is divided into two parts: the hard outer part consists of small cells containing oil, the inner part has large and relatively soft cells. Except for cases where coffee has only 1 bean, or rarely has 3 beans, most coffee beans have 2 equal parts
Chemical composition of coffee beans
In a complete coffee, there will be many different ingredients, each of which is very important to create the flavor of the coffee bean.
Peel
The peel of the coffee fruit contains a lot of anthocyanins, so when ripe the fruit is often red. In addition, the fruit peel also contains many substances such as caffeine, Alkaloids, Tannins and many other enzymes.
Meat shell
The fleshy shell contains mainly viscous substances and soft cells. This part contains a lot of sugar, making the coffee taste sweet, and also contains a substance that supports the fermentation process Pectinase, making the taste of the coffee bean better.
Rice husk
Because it is wrapped right outside the kernel, the husk layer also inherits a significant amount of caffeine, up to 0.4% of the weight of the coffee fruit.
Coffee beans
In fully ripe coffee beans, the amount of water accounts for 10 - 12%, then 10 - 13% Lipid, 9 - 11% Protein, 5 - 10% sugar and 3 - 5% starch. Each type of coffee has a different chemical composition that creates a unique flavor. In addition, if processed optimally, it will also greatly improve quality.
Characteristics of substances contained in coffee beans
Water
When dried, standard coffee must have 10 - 12% water in bound form. After roasting, this number is about 2 - 3%. When the amount of water is greater, preservation will be extremely difficult. Coffee beans will be moldy, seriously affecting the quality.
Lipids
Of the 10 - 13% lipids of coffee beans, up to 90% are oils, the rest are waxes. This is the ingredient that creates the aroma and viscosity of coffee. After processing, the amount of Lipid remaining is very little and sticks to the coffee grounds. Use this residue to nourish your skin very well.
The protein
Although the protein in coffee is low, it has many good amino acids. When roasted, this protein will burn and create the characteristic aroma and flavor of coffee due to the contribution of this ingredient.
Minerals
The mineral content in coffee beans ranges from 3 - 5%, mainly types such as Magnesium, Potassium, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Chlorine, Iron, Sulfur, etc. Good coffees often have very little mineral content because they affect the quality of coffee beans. Not good for the taste of coffee.
Caffeine
This is the characteristic that makes coffee different from other fruits and nuts. Caffeine is the source of the benefits from drinking coffee, helping you feel relaxed and energized. The amount of caffeine in different types of coffee is different, with Robusta having the highest amount of caffeine.
S54 Coffee
